I. Introduction to MRCOG Pathway for IMGs
A. Overview of the MRCOG (Membership of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists)
The MRCOG is a prestigious qualification offered by the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists in the UK. It is designed for medical professionals aspiring to specialize in Obstetrics and Gynecology. The MRCOG pathway consists of three parts: Part 1, Part 2, and Part 3 examinations, each assessing different aspects of knowledge, clinical skills, and professional competence in the field.
Part 1 MRCOG:
Part 1 focuses on assessing the candidate’s understanding of basic sciences relevant to Obstetrics and Gynecology. It covers a wide range of topics including anatomy, physiology, embryology, and relevant medical principles. This part is a multiple-choice exam designed to test theoretical knowledge.
Part 2 MRCOG:
Part 2 evaluates clinical knowledge, problem-solving abilities, and decision-making skills related to Obstetrics and Gynecology. It consists of both written and oral components, testing clinical scenarios, critical analysis, and evidence-based practice.
Part 3 MRCOG:
Part 3 is a clinical assessment that evaluates the candidate’s ability to apply theoretical knowledge and clinical skills in practical settings. It involves structured oral examinations, simulations, and scenarios that mirror real clinical situations.
B. Importance of MRCOG Pathway for IMGs aspiring to become Obstetricians/Gynecologists in the UK
For IMGs aiming to pursue a career as Obstetricians/Gynecologists in the UK, obtaining the MRCOG qualification is crucial. It not only serves as a benchmark of competency and proficiency in the field but also enhances career prospects and opportunities.
The MRCOG is widely recognized and respected globally, providing IMGs with a standardized qualification that demonstrates their proficiency in Obstetrics and Gynecology according to UK standards. This qualification significantly enhances an IMG’s credibility, making them more competitive in the job market, especially when applying for training programs and consultant positions within the National Health Service (NHS) or other healthcare institutions in the UK.
II. Prerequisites for IMGs
A. Medical Qualification Recognition:
Before embarking on the MRCOG pathway, International Medical Graduates (IMGs) need to ensure their medical qualifications are recognized by the General Medical Council (GMC) in the UK. The GMC evaluates and verifies medical degrees from foreign institutions to ensure they meet the required standards for practice in the UK. IMGs must undergo the process of GMC registration, which involves providing evidence of their qualifications, completing necessary examinations if required, and demonstrating proficiency in English through exams like the International English Language Testing System (IELTS) or Occupational English Test (OET).
Validating Medical Degrees:
IMGs need to submit their qualifications and relevant documents to the GMC for assessment. Depending on the country of study, some IMGs might be required to sit for the Professional and Linguistic Assessments Board (PLAB) test or an equivalent exam to demonstrate their medical knowledge and skills.
International English Language Testing System (IELTS) Requirements:
Proficiency in English is a prerequisite for medical practice in the UK. IMGs need to achieve a certain score in the IELTS exam (or an equivalent English language test) to demonstrate their language proficiency. The GMC sets specific criteria for language proficiency, and meeting these standards is essential for GMC registration.
B. Preparation for MRCOG Examinations:
Preparation for the MRCOG exams requires a comprehensive approach. IMGs should familiarize themselves with the exam structure, syllabus, and recommended study materials for each part of the MRCOG.
Part 1 MRCOG Preparation:
Studying foundational sciences, including anatomy, physiology, and embryology, is essential for success in Part 1. IMGs can utilize resources such as textbooks, online courses, and question banks specifically tailored to the Part 1 syllabus. Practice exams and mock tests are also beneficial for assessing knowledge and improving exam-taking skills.
Part 2 MRCOG Preparation:
Part 2 demands a deeper understanding of clinical scenarios, evidence-based practice, and decision-making skills. IMGs should engage in clinical rotations, case discussions, and interactive study sessions. Reviewing past papers, case-based discussions, and attending preparatory courses can significantly enhance readiness for this comprehensive examination.
Part 3 MRCOG Preparation:
Part 3 involves practical application of knowledge and clinical skills. IMGs should engage in hands-on clinical experience, role-play scenarios, and structured mock exams to simulate real clinical encounters. Participating in communication skills workshops and receiving feedback from mentors or peers can aid in refining clinical and communication abilities required for this exam.
III. MRCOG Examination Structure
A. Part 1 MRCOG:
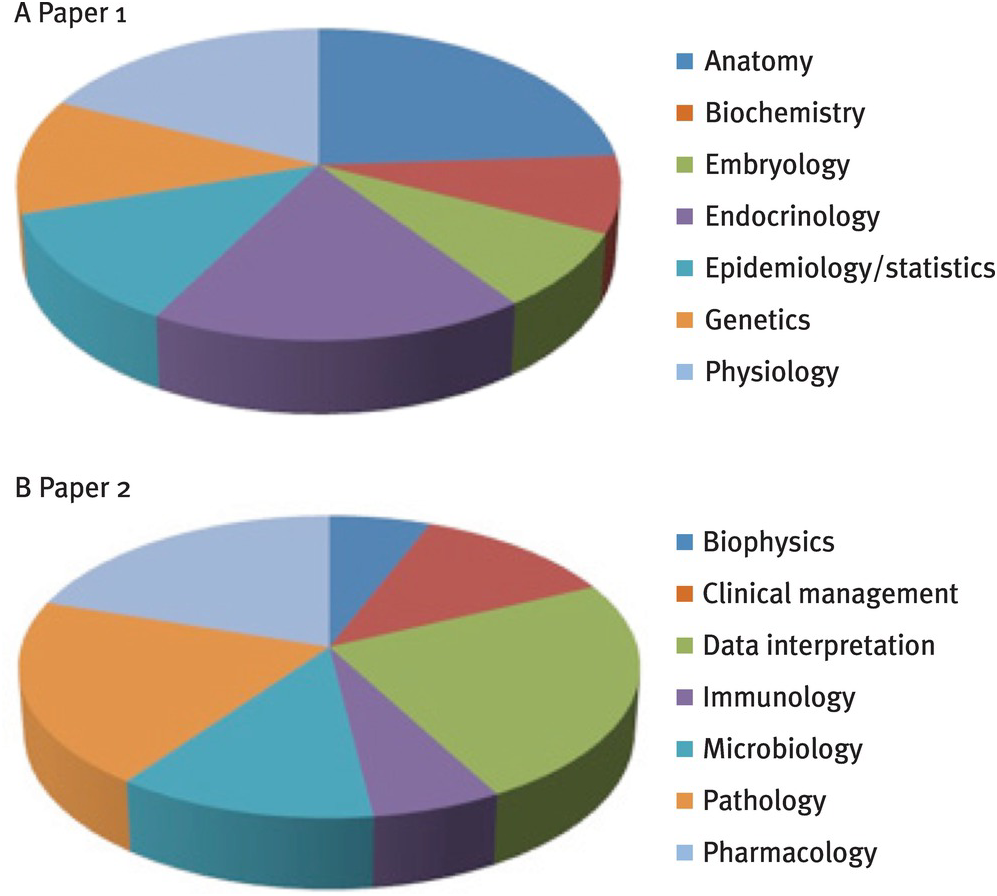
The Part 1 MRCOG examination is a crucial step in the MRCOG pathway, designed to assess an individual’s understanding of fundamental scientific principles relevant to Obstetrics and Gynecology. The exam structure primarily consists of multiple-choice questions (MCQs) covering a broad spectrum of topics, including anatomy, physiology, embryology, and basic clinical sciences.
Syllabus and Subjects Covered:
The syllabus for Part 1 MRCOG is comprehensive, encompassing key foundational sciences essential for Obstetrics and Gynecology practice. Topics include reproductive physiology, endocrinology, genetics, fetal development, maternal physiology, and basic epidemiology relevant to women’s health.
Exam Format and Assessment Criteria:
The exam typically comprises a series of MCQs, evaluating candidates’ knowledge and understanding of the syllabus content. Questions may focus on diagnosis, management, and treatment options related to Obstetrics and Gynecology. Candidates are assessed on their ability to apply theoretical knowledge to clinical scenarios and make appropriate decisions.
Preparation Tips and Recommended Study Materials:
To excel in Part 1, IMGs should adopt a structured study approach. Utilizing reputable textbooks, online resources, and practice question banks aligned with the MRCOG Part 1 syllabus is essential. Joining study groups, attending preparatory courses, and participating in revision sessions can enhance understanding and retention of key concepts. Consistent practice through mock exams is also recommended to gauge progress and improve exam-taking skills.
B. Part 2 MRCOG:
Part 2 of the MRCOG examination assesses clinical knowledge, problem-solving abilities, and decision-making skills within the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology. It consists of written and oral components, designed to evaluate candidates’ clinical reasoning and application of theoretical knowledge in clinical scenarios.
Detailed Breakdown of the Curriculum:
Part 2 covers a wide array of topics related to women’s health, including obstetric emergencies, gynecological conditions, antenatal care, labor management, gynecological malignancies, and reproductive medicine. Candidates are expected to demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of clinical presentations, investigations, and management strategies for various obstetric and gynecological conditions.
Exam Format:
The written component typically involves essay-based questions, short-answer questions, and objective structured clinical examination (OSCE)-style stations. Candidates must showcase their ability to analyze clinical scenarios, formulate differential diagnoses, and propose appropriate management plans.
Strategies for Success and Suggested Resources for Preparation:
Success in Part 2 requires a combination of clinical experience, critical thinking, and structured preparation. IMGs should actively engage in clinical rotations, case discussions, and OSCE practice sessions to refine clinical skills. Reviewing past papers, attending preparatory courses, and utilizing online resources specifically tailored to MRCOG Part 2 can aid in thorough preparation for this comprehensive examination.
C. Part 3 MRCOG:
1. Clinical Assessment Overview:
Part 3 of the MRCOG is a clinical assessment that evaluates candidates’ ability to apply theoretical knowledge and clinical skills in real-life scenarios. It assesses communication skills, decision-making abilities, and professionalism in a clinical setting.
The assessment involves structured oral examinations conducted in various stations where candidates encounter simulated clinical scenarios or patient encounters. These stations simulate different aspects of clinical practice, such as history-taking, patient management, counseling, and teamwork.
2. Structured Oral Examination Details:
Part 3 comprises multiple stations, each presenting a specific clinical scenario or interaction with a simulated patient. Candidates rotate through these stations within a defined timeframe, addressing different scenarios or tasks at each station.
The examiners assess candidates based on their approach to the clinical scenario, including history-taking, examination skills, diagnostic reasoning, management plans, communication with patients and colleagues, ethical considerations, and professionalism.
3. Recommended Study Approaches and Preparation Guidance:
Preparation for Part 3 requires a multifaceted approach that integrates theoretical knowledge, clinical experience, and communication skills development.
- Clinical Experience: Actively engaging in clinical practice, observing consultations, and participating in patient care during rotations is invaluable. It helps in developing clinical acumen and enhances communication skills.
- Communication Skills Workshops: Attending workshops or courses focused on communication skills, breaking bad news, and patient counseling can significantly improve the candidate’s ability to communicate effectively with patients and colleagues.
- Mock Examinations: Participating in mock oral examinations or role-playing scenarios can simulate the exam environment, providing an opportunity to practice clinical reasoning, communication, and time management skills.
- Structured Preparation Courses: Joining structured preparatory courses specifically designed for MRCOG Part 3 can offer guidance on approaching different scenarios, understanding the expectations of examiners, and improving overall performance in the examination.
Candidates should focus not only on clinical knowledge but also on the holistic approach to patient care, ethical considerations, and effective communication, as these are integral components of success in the Part 3 MRCOG examination.
IV. Training and Work Experience
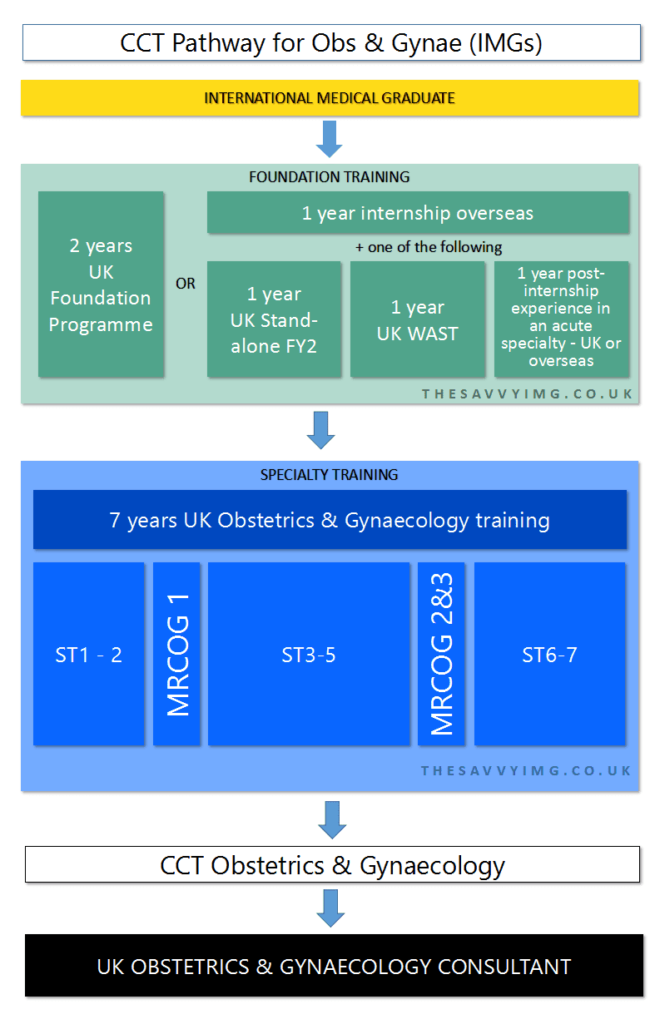
A. Foundation Training:
Understanding Foundation Programme Applications for IMGs:
Foundation Training serves as an essential phase in the career progression of doctors in the UK. For IMGs, applying to the Foundation Programme involves meeting specific criteria, including GMC registration and eligibility for work in the UK. It typically comprises two years of supervised clinical training, providing exposure to various specialties, including Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Required Competencies and Experience during Foundation Years:
The Foundation Programme aims to develop core clinical skills, professionalism, and teamwork abilities. IMGs need to demonstrate competence in essential areas such as patient care, communication, clinical reasoning, and professionalism. Rotations through different specialties offer a broad understanding of healthcare systems and patient management.
B. Core Training in Obstetrics and Gynecology:
Outlining Core Training Programs in the UK:
After completing the Foundation Programme, doctors can progress to Core Training in Obstetrics and Gynecology. This training focuses on developing specialized skills and knowledge relevant to the field. Core training typically lasts two to three years and involves rotations in various Obstetrics and Gynecology specialties.
Entry Requirements and Application Procedures for IMGs:
IMGs interested in Core Training should apply through formal application processes, adhering to specific eligibility criteria. This may include possessing the MRCOG Part 1 qualification, GMC registration, and meeting other requirements set by the training programs or deaneries.
Rotations, Placements, and Duration of Core Training:
Core Training offers rotations through different subspecialties within Obstetrics and Gynecology, such as maternal-fetal medicine, reproductive medicine, gynecological oncology, and urogynecology. The duration and structure of these rotations vary but provide a comprehensive exposure to various aspects of the field.
C. Specialty Training:
Eligibility Criteria for Specialty Training:
Upon successful completion of Core Training, doctors can progress to Specialty Training. IMGs must fulfill specific criteria, including completion of MRCOG Part 2 and demonstrating competencies in Obstetrics and Gynecology to enter Specialty Training.
Applying for Specialty Training Posts and Pathways Available for IMGs:
IMGs can apply for specialty training posts through national recruitment processes or deanery-specific applications. Various pathways exist for specialty training, allowing individuals to focus on specific areas of interest within Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Duration and Components of Specialty Training:
Specialty Training typically spans four to six years and provides in-depth, specialized training in areas like maternal medicine, gynecological oncology, reproductive medicine, and fetal medicine. The training involves supervised clinical practice, research opportunities, and development of advanced skills essential for consultant-level practice.
Navigating through Foundation, Core, and Specialty Training is integral for IMGs aspiring to excel in Obstetrics and Gynecology within the UK healthcare system. Each phase offers distinct learning experiences and skill development crucial for advancing in the field.
VI. Registration and Certification
A. Obtaining Full GMC Registration:
1. Steps Involved in Gaining Full Registration:
Gaining full General Medical Council (GMC) registration is a significant milestone for doctors aiming to practice in the UK. The process involves several steps:
- Completion of Necessary Examinations: Candidates must have completed all required exams, which may include PLAB for IMGs, if applicable.
- Provision of Required Documentation: Submission of necessary documents such as primary medical qualification, evidence of language proficiency, and verification of medical credentials.
- Provisional Registration: Some IMGs might initially receive provisional registration, which can be converted to full registration upon meeting specific requirements.
2. Required Documentation and Examinations:
- Primary Medical Qualification: Certified documentation verifying the medical degree obtained from a recognized institution.
- Language Proficiency: Evidence of meeting the GMC’s language proficiency requirements, typically through exams like IELTS or OET.
- Professional and Educational Certificates: Documentation showcasing completion of required exams and any additional certifications relevant to medical practice.
B. Attaining the MRCOG:
1. Completing All Parts of the Examination:
Completion of all three parts of the MRCOG examination is necessary to attain the MRCOG qualification. This involves:
- Successful completion of Part 1, assessing theoretical knowledge.
- Passing Part 2, evaluating clinical knowledge and problem-solving abilities.
- Demonstrating competence in Part 3, focusing on practical application of skills in clinical scenarios.
2. Issuance of the MRCOG Certification:
Upon successful completion of all three parts of the MRCOG examination, candidates are awarded the MRCOG qualification by the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. The certification acknowledges the candidate’s proficiency and competence in Obstetrics and Gynecology based on UK standards. This certification significantly enhances the credibility and career prospects of doctors aspiring to practice as Obstetricians/Gynecologists in the UK.
Gaining both full GMC registration and the MRCOG certification are crucial milestones for IMGs aiming to establish themselves as qualified and competent practitioners in Obstetrics and Gynecology within the UK healthcare system. These achievements validate their skills, knowledge, and readiness for consultant-level roles within the field.
VII. Career Prospects and MRCOG Pathways
A. Consultant Positions:
1. Application and Selection Process for Consultant Positions:
- Application Criteria: Eligibility for consultant positions typically requires completion of specialty training, possession of the MRCOG qualification, and full GMC registration.
- National Recruitment: Consultant positions often involve participating in national recruitment processes organized by the NHS or respective deaneries. This may include submission of applications, interviews, and assessments.
- Selection Criteria: Candidates are evaluated based on their clinical expertise, experience, leadership abilities, and contributions to the field through research or teaching.
2. Career Progression and Specialties within Obstetrics/Gynecology:
- Career Advancement: Consultants in Obstetrics and Gynecology have opportunities for career advancement through senior positions, including lead consultant roles, clinical directorships, or managerial positions within healthcare institutions.
- Specialization: Within Obstetrics and Gynecology, consultants can choose to specialize in various areas such as maternal-fetal medicine, gynecological oncology, reproductive medicine, urogynecology, and fertility.
B. Private Practice and Academic Opportunities:
1. Exploring Private Practice Options:
- Establishing Private Practice: Consultants in Obstetrics and Gynecology often have the option to establish their private practice, offering specialized services to patients outside the NHS.
- Collaboration with Private Healthcare Providers: Collaboration with private hospitals or healthcare facilities allows consultants to offer their expertise and services in a private setting.
2. Opportunities in Academia, Teaching, and Research:
- Academic Positions: Consultants can pursue academic roles in universities or medical schools, engaging in teaching, mentoring students, and conducting research.
- Research Opportunities: Engaging in research projects, clinical trials, and publications within Obstetrics and Gynecology offers consultants opportunities to contribute to advancements in the field.
The career prospects for consultants in Obstetrics and Gynecology encompass a diverse range of opportunities within the NHS, private practice, academia, and research. Consultants can progress in their careers by specializing in specific areas, taking on leadership roles, contributing to research, and expanding their scope of practice within the field.
VIII. Resources and Support for IMGs
A. Support Networks and Associations:
1. Accessing Support from IMG Communities and Networks:
- IMG Communities: IMGs can benefit from joining communities and networks specifically tailored to support international medical graduates. These platforms provide guidance, share experiences, and offer advice on navigating the challenges faced during the MRCOG pathway and integration into the UK healthcare system.
- Online Forums and Groups: Various online forums, social media groups, and platforms exist where IMGs can connect with peers, share resources, and seek advice on exam preparation, training programs, and career progression.
2. Involvement in Relevant Professional Associations:
- Professional Associations: Joining professional associations such as the British Medical Association (BMA) or specialty-specific societies like the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) provides IMGs with access to resources, training opportunities, and networking events. These associations offer valuable support, advocacy, and guidance for career development.
B. Mentorship and Guidance:
1. Importance of Mentorship for IMGs:
- Guidance and Support: Mentorship plays a pivotal role in assisting IMGs throughout their MRCOG journey and beyond. A mentor, typically an experienced healthcare professional, offers guidance, advice, and support, aiding in navigating challenges, setting career goals, and making informed decisions.
- Career Development: Mentors provide insights into the UK healthcare system, offer advice on training programs, exam preparation strategies, and help in building professional networks.
2. Seeking Guidance and Mentorship throughout the MRCOG Pathway:
- Identifying Mentors: IMGs can seek mentors within their training programs, professional associations, or through networking platforms. They should look for individuals who have successfully completed the MRCOG pathway and have experience in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
- Regular Interaction: Establishing regular communication and seeking guidance from mentors at various stages of the MRCOG pathway helps in setting goals, overcoming challenges, and making informed career decisions.
Accessing support networks, engaging in professional associations, and seeking mentorship are integral components of success for IMGs pursuing the MRCOG pathway. These resources provide guidance, encouragement, and a supportive community to navigate the challenges and complexities of training and practicing in Obstetrics and Gynecology within the UK.
IX. Conclusion
A. Recap of the MRCOG Pathway for IMGs:
The MRCOG pathway for International Medical Graduates (IMGs) aspiring to become Obstetricians/Gynecologists in the UK is a rigorous yet rewarding journey. It involves:
- Validating medical qualifications through the GMC, including demonstrating proficiency in English.
- Progressing through three parts of the MRCOG examination, covering theoretical knowledge, clinical skills, and practical application.
- Undertaking foundational training, core training in Obstetrics and Gynecology, and specialty training to gain comprehensive clinical experience and expertise.
- Attaining full GMC registration and the prestigious MRCOG certification, which mark significant milestones in professional development.
B. Encouragement and Advice for Those Pursuing a Career in Obstetrics/Gynecology in the UK:
For IMGs pursuing a career in Obstetrics/Gynecology in the UK, perseverance, dedication, and continuous learning are key. Some advice includes:
- Persistence: Embrace challenges along the MRCOG pathway with determination and resilience. Each hurdle is an opportunity to learn and grow.
- Engage and Network: Connect with fellow IMGs, mentors, and professional associations to access support, guidance, and valuable resources.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated with advancements in the field, engage in professional development, and remain committed to lifelong learning.
- Seek Mentorship: Find mentors who can provide insights, advice, and support throughout the journey, aiding in making informed career decisions.
- Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledge and celebrate each accomplishment, whether passing an exam, completing training, or achieving certification.
Pursuing a career in Obstetrics/Gynecology in the UK as an IMG is an enriching journey that offers opportunities for personal and professional growth. Embrace the challenges, leverage the available resources, and stay dedicated to achieving your goals in this fulfilling medical specialty.
Below are listed a few more articles you might be interested in if you are an IMG looking for different careers in health and also pathway that you might follow. If you have any questions you can comment them down below and they will be answered. May you achieve that what you dream.
Post-MBBS Opportunities Worldwide in 2023: The Ultimate Guide
Moving to UK as a doctor with PLAB in 2023 [Everything Guide]